可预测的状态管理库 - redux
Redux 是 JavaScript 状态容器,提供可预测化的状态管理。中文文档
什么是可预测的状态管理
数据在 什么时候, 因为什么, 发生了 什么改变, 都是 可以控制和最终的, 我们就称之为 可预测的状态管理
为什么使用 redux?
- React 是通过数据来驱动界面更新的, React 负责更新界面, 而我们只需要负责管理相应的数据(状态)
- 随着页面越来越复杂, 我们需要在不同的组件中共享一些状态, 而且状态还可能存在依赖关系
- 在程序相对复杂的时候, 想要很要很好的知道
什么时候改变为什么改变改变了什么状态就需要用到redux
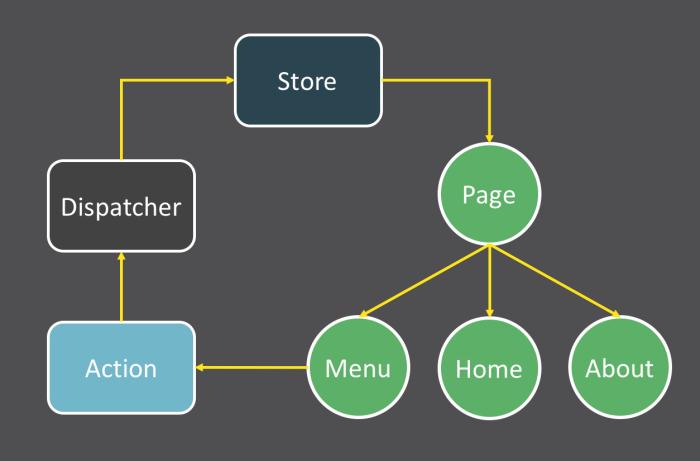
redux 三大核心
- 通过 Store 来保存状态
- 所有状态不能直接修改, 只能通过 action 来修改
- 通过 reducer 将 store 和 action 串联起来
redux 基本使用
js
const redux = require("redux");
// 1.定义一个状态
const initState = {
count: 0,
};
// 2.利用 store 来保存状态
const store = redux.createStore(reducer);
// 3.利用 action 修改状态
const incrmentAction = { type: "incrment", payload: { num: 1 } };
const decrmentAction = { type: "decrment", payload: { num: 1 } };
// 4.利用 reducer 串联 store 和 action
function reducer(state = initState, action) {
const { type, payload } = action;
const newState = {};
newState.count = state.count;
switch (type) {
case "incrment": // +1
newState.count += payload.num;
break;
case "decrment": // -1
newState.count -= payload.num;
break;
}
return newState;
}
// 5.监听 state 状态变化
store.subscribe(() => {
// 获取 store 中的 state 状态
console.info("state 发生变化了:", store.getState());
});
// 触发修改, 让 state 中的值发生变化
store.dispatch(incrmentAction);react-redux 和 redux 的关系
- redux 是一个状态管理的库, 在任何 js 环境中都能使用
- react-redux 是一个
基于 redux 并且专为 react 设计的状态管理库
在 react 中使用 react-redux
文档资料
安装
sh
yarn add redux react-redux
# or
npm i redux react-redux创建相关文件
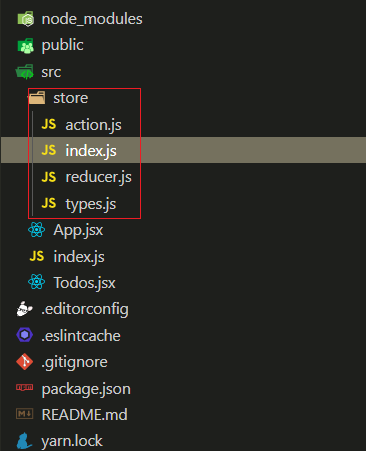
代码实现
组件部分
- src/index.js
jsx
import React from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import store from "./store/index";
import App from "./App.jsx";
render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
document.getElementById("root")
);- src/app.jsx
jsx
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { createTodoAction } from "./store/action";
import Todos from "./Todos";
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.todoRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Todos />
<div>
<input ref={this.todoRef} type="text" />
<button onClick={() => this.addTodo()}>添加任务</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}
// 添加TODO
addTodo() {
const content = this.todoRef.current.value.trim();
if (!content) {
alert("任务内容不能为空");
return;
}
const todos = this.props.todos || [];
const isExists = todos.find((item) => item.content === content);
if (isExists) {
alert("任务已经存在");
return;
}
const lastId = todos[todos.length - 1].id || 0;
this.props.createTodo(lastId + 1, content);
this.todoRef.current.value = "";
}
}
// 将 store 中保存的 todos 映射到 props 上
// 也就是说, 在组件中可以直接使用 this.props.todos 就能
// 直接访问到 store 中保存的 todos
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
todos: state.todos,
};
};
// 因为是直接返回一个对象: 有的人会利用 js 箭头函数的特性,
// 省略 retuen 语句, 但只写 {} 就无法识别, 所以必须 => ({})
// 使用 connect 将这个组件和react-redux连接起来后, 会
// 将这个 mapDispatchToProps 中返回对象上的所有方法
// 映射到组件的 props 上, 也就是说可以使用 this.props.createTodo
// 来调用这个方法
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
createTodo: (id, content) => dispatch(createTodoAction({ id, content })),
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(App);- src/Todos.jsx
jsx
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { removeTodoAction } from "./store/action";
class Todos extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
const todos = this.props.todos || [];
return (
<ul>
{
/* 直接遍历 props 中的 todos */
todos.map((item) => {
return (
<li key={item.id}>
<span>{item.content}</span>
<button onClick={() => this.props.removeTodoById(item.id)}>
删除
</button>
</li>
);
})
}
</ul>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
todos: state.todos,
});
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
removeTodoById: (id) => dispatch(removeTodoAction(id)),
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(Todos);store 部分
- src/store/index.js
js
import { createStore } from "redux";
import reducer from "./reducer.js";
const store = createStore(
reducer,
// 检查是否安装调试工具, 开启调试
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);
export default store;- src/store/reducer.js
js
import * as types from "./types";
const initState = {
todos: [
/*{ id: 101, content: "今天学习react-redux" }*/
],
};
const reducer = (state = initState, action) => {
const { type, payload } = action;
const newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state));
switch (type) {
case types.CREATE_TODO: // 增加 TODO
newState.todos.push(payload);
break;
case types.REMOVE_TODO: // 删除 TODO
newState.todos = newState.todos.filter((item) => item.id !== payload.id);
break;
default:
console.info("未知的 Action Type!", type);
}
return newState;
};
export default reducer;- src/store/types.js
js
// 增加TODO
export const CREATE_TODO = "create_todo";
// 删除TODO
export const REMOVE_TODO = "remove_todo";- src/store/action.js
js
import * as types from "./types";
// 创建 todo
export const createTodoAction = (payload) => ({
type: types.CREATE_TODO,
payload,
});
// 删除 todo
export const removeTodoAction = (id) => ({
type: types.REMOVE_TODO,
payload: { id },
});react-redux 的实现原理
js
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import React from "react";
const StoreCtx = React.createContext({});
export const Provider = StoreCtx.Provider;
export const connect = (mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) => (Wrapper) => {
class AdvComponent extends React.PureComponent {
constructor(props, ctx) {
super(props, ctx);
this.state = {
storeState: { ...mapStateToProps(this.context.getState()) },
};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.context.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
storeState: { ...mapStateToProps(this.context.getState()) },
});
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.context.unsubscribe();
}
render() {
return (
<Wrapper
{...this.props}
{...mapStateToProps(this.context.getState())}
{...mapDispatchToProps(this.context.dispatch)}
/>
);
}
}
AdvComponent.contextType = StoreCtx;
return AdvComponent;
};使用与官方
react-redux不同的是:
jsx
import React from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import App from "./App.jsx";
import { Provider } from "./react-redux";
import store from "./store/index";
render(
<React.StrictMode>
{/* 注意: 此处用的是 value 而不是 store, 其他的和官方的 react-redux 使用没有什么不同 */}
<Provider value={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById("root")
);redux-thunk 中间件
什么是中间件, 为什么要使用中间件?
可以在 action 被派发到 reducer 之前做一些额外的操作, 这个操作的函数就叫中间件
使用中间件, 可以降低代码耦合性, 提高代码的可维护性
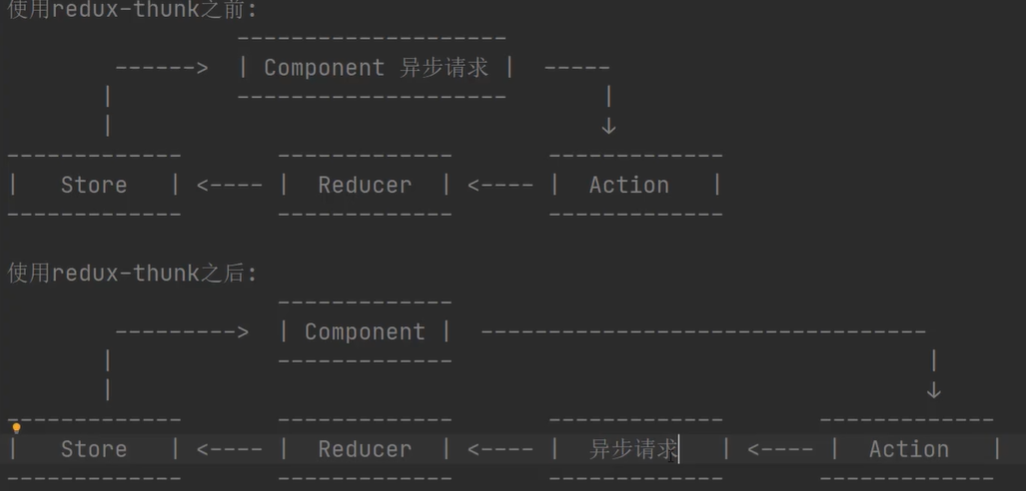
默认情况下, dispatch 方法只能接收一个对象, 如果想让 dispatch 除了可以接收对象以外还可以接收方法, 那么我们可以使用 redux-thunk 中间件 redux-thunk 中间件的作用: 可以让 dispatch 接收一个函数, 可以让我们在通过 dispatch 派发任务的时候去执行这个传递的函数
1.安装
sh
yarn add redux-thunk
# or
npm i redux-thunk2.在 store 应用中间件 src/store/index.js
js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware, compose } from "redux";
import reducer from "./reducer.js";
import ReduxThunk from "redux-thunk";
// 检测是否有浏览器调试插件
const composeEnhancers =
typeof window === "object" && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__
? window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({})
: compose;
// 应用中间件
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(applyMiddleware(ReduxThunk));
const store = createStore(reducer, enhancer);
export default store;- 使用
- src/App.jsx
jsx
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { getRecomPlayListAction } from "./store/action";
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<div>
<button onClick={() => this.props.getRecomPlayList()}>
获取网易云音乐推荐歌单
</button>
</div>
{/* 获取到的数据: */}
<div>
<pre>{JSON.stringify(this.props.recomPlayList, "", 4)}</pre>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
recomPlayList: state.recomPlayList,
});
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
getRecomPlayList: () => dispatch(getRecomPlayListAction),
});
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(App);- src/store/action.js
js
import * as types from "./types";
/**
* 获取推荐歌单 action, 如果已经获取了, 就不获取了
* @param {Function} dispatch 派发 action
* @param {Function} getState 用于获取 store 中的 state
*/
export const getRecomPlayListAction = (dispatch, getState) => {
const state = getState();
if (state.recomPlayList.length) {
return;
}
const url = "http://musicapi.liaohui5.cn/personalized?limit=10";
fetch(url)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((data) => {
const action = {
type: types.GET_RECOM_PLAY_LIST,
payload: [],
};
if (data.code !== 200) {
console.log("响应数据有误", data);
} else {
action.payload = data.result;
}
dispatch(action);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.info("请求出错了...", error);
});
};- src/store/reducer.js
js
import * as types from "./types";
const initState = {
recomPlayList: [], // 推荐歌单
};
const reducer = (state = initState, action) => {
const newState = { ...state };
const { type, payload } = action;
switch (type) {
case types.GET_RECOM_PLAY_LIST: // 获取推荐歌单
newState.recomPlayList = payload;
break;
default:
console.info("未知的 Action Type!", type);
}
return newState;
};
export default reducer;redux-saga 中间件
- redux-saga 和 redux-thunk 功能类似, 只是使用方法上有些不同
自定义 redux 中间件
- 定义中间件, 中间件的原理图
js
/**
* 中间件的本质就是一个函数, 如果在 store 中应用这个中间件,
* 那么在所有的 action 派发后, 不会直接执行 reducer 而是会
* 先依次执行完所有的中间件, 然后再执行 reducer
*
* @param {Object} store 包含两个方法, dispatch 和 getState
* @param store.dispatch: 派发 action
* @param store.getState: 获取当前 store 的所有状态
*/
let reduxLogger = (store) => {
/**
* @param {Function} next 如果本中间件执行完了, 需要调用这个方法去执行下一个中间件
*/
return (next) => {
/**
* @param action 当前 action 信息
*/
return (action) => {
// 中间件的逻辑代码
};
};
};
// 这种写法是上面那种写法的简写形式, 上面那种写法只是为了写注释 ٩(๑>◡<๑)۶
reduxLogger = (store) => (next) => (action) => {
console.log(`${action.type}执行前的 state:`, store.getState());
next(action);
console.log(`${action.type}执行后的 state:`, store.getState());
};
export default reduxLogger;- 在 store 中应用中间件
js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import reducer from "./reducer.js";
import ReduxThunk from "redux-thunk";
import ReduxLogger from "./reduxLogger";
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(ReduxThunk, ReduxLogger));
export default store;优化 reducer
- 目录结构: 拆分 reducers 和 actions
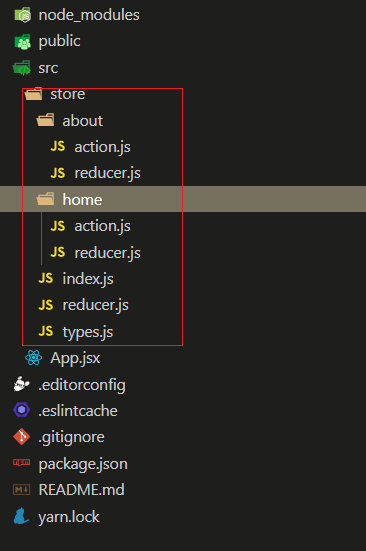
- 合并 reducers
js
import { combineReducers } from "redux";
import homeReducer from "./home/reducer";
import aboutReducer from "./home/reducer";
// 将拆分开的 reducer 合并
const reducer = combineReducers({
homeReducer,
aboutReducer,
});
export default reducer;