前置知识
函数其实是特殊的对象
在 JavaScript 中, 函数其实是一种特殊的对象, 可能和其他的语言不太一样, 虽然大多数时候都是用 function 关键字去定义函数的, 但是其实我们可以也可以利用 Function 构造器来创建函数实例
function sum1(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
const sum2 = new Function('x,y', 'return x + y');
sum1(1, 2); // 3
sum2(1, 2); // 3Function 实例对象有哪些属性?
能够访问的:
- 推荐阅读 MDN 文档
arguments: 参数列表对象(已废弃,不推荐使用)name: 函数名称function f1(){}这个实例对象的名称就是f1length: 函数的参数(形参)总数prototype: 实例对象的原型对象
无法访问的:
[[Scopes]]这个属性是存储函数作用域链的容器, 保存的就是作用域链
- 作用域链 中保存的是
全局执行上下文 GO和函数执行期上下文 AO - 当函数执行完之后, 函数执行期上下文 会自动销毁, 再次执行函数时, 会重新生成一个新的 函数执行期上下文
console.dir(function fn() {}); // 在浏览器的 Console 中执行, 然后点开查看所有属性什么是作用域
所谓作用域就是变量可以访问的区域范围, 在JavaScript中, 主要有3种作用域
- 全局作用域
- 函数作用域(ESM/CommonJS 模块也算)
- 块级作用域(ES6新增内容)
// 全局作用域, 在浏览器中也可以直接通过 window.str 来访问
var str = 'hello-world';
console.log(window.str); // 'hello-world'
// 函数作用域, 只在这个 f1 函数体内有效
function f1() {
var str = 'hello-f1';
console.log(str);
}
console.log(str); // 在外界无法访问 f1 内部的函数? 思考为什么?
// 块级作用域, 必须是 let const 指令声明的变量才行, 因为 var 指令会在预编译阶段 "变量提升"
{
let a = 1;
const b = 2;
var c = 3;
}
// console.log(a); // ReferenceError: a is not defined
// console.log(b); // ReferenceError: a is not defined
console.log(c); // 3什么是作用域链
在 JavaScript 中作用域链是指变量的可访问性和查找规则, 它是由嵌套的作用域形成的一个链式结构(类似链表)
在使用一个变量的时候, JavaScript 执行引擎首先会在当前作用域查找是否有这个变量, 如果有就直接使用, 如果没有 就会沿着作用域链一级一级的向上查找
const a = 1;
function f1() {
const b = 2;
function f2() {
const c = 3;
return a + b + c + d;
// a: 在 f2 函数作用域中查找, 没有, 再到 f1 函数作用域中查找, 没有, 再到全局作用域中查找, 找到了就使用
// b: 在 f2 函数作用域中查找, 没有找到, 再到 f1 函数作用域中查找, 找到了就使用
// c: 在 f2 函数作用域中查找, 找到了就使用
// d: 在 f2 函数作用域中查找, 没有, 再到 f1 函数作用域中查找, 没有, 再到全局作用域中查找, 没找到就报错
}
return f2();
}
f1(); // ReferenceError: d is not defined作用域链分析
函数的的作用域链在代码预编译阶段就已经初始化完成
function a() {
function b() {
var b = 2;
}
var a = 1;
b();
}
var c = 3;
a();0: 预解析阶段, 初始化GO和作用域链
第1步: a函数声明, 初始化作用域链

第2步: a函数声明, 将 AO(a函数闭包)放入作用域链
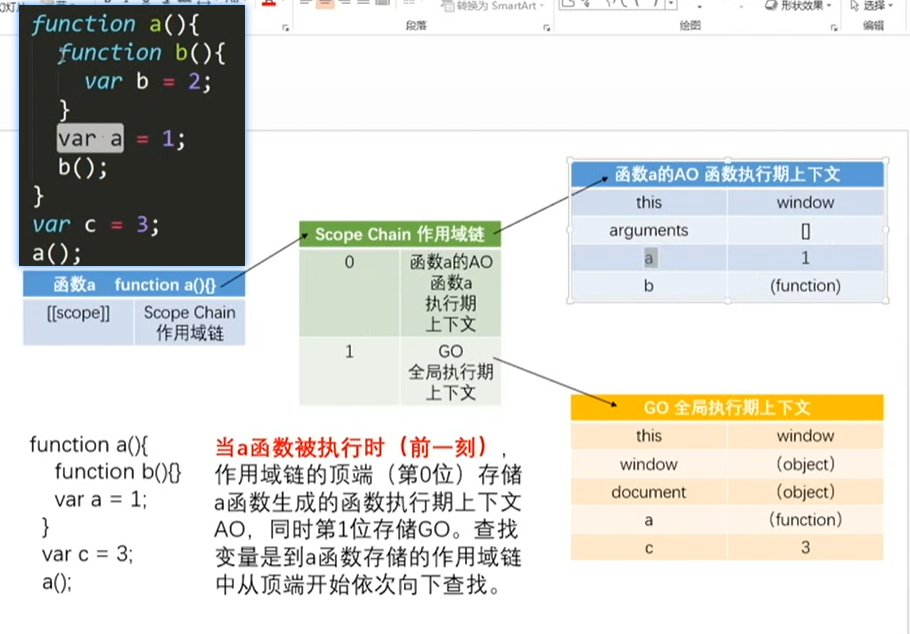
第3步: 当b函数被执行时
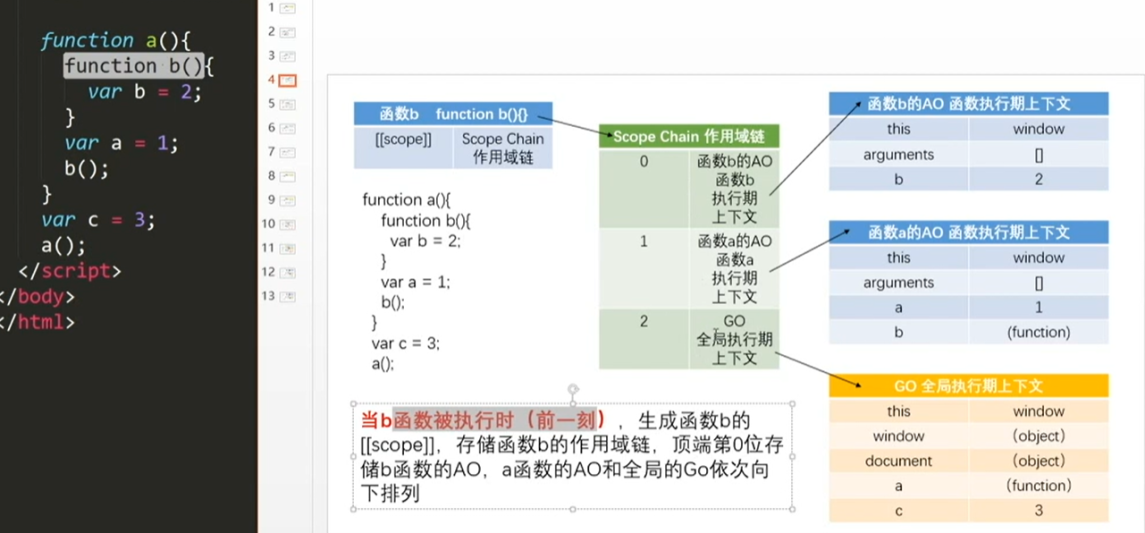
第4步: 当内部b函数执行完成的时候
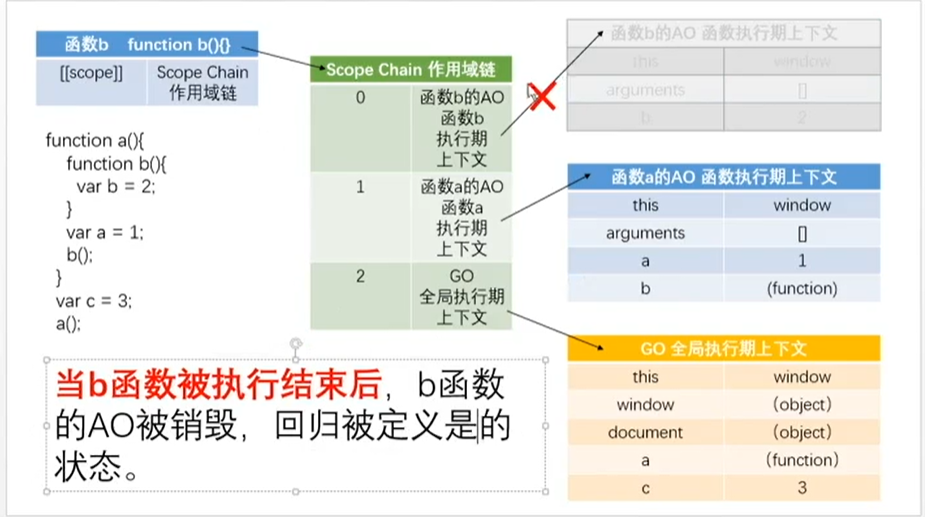
第5步: 当 a 函数被执行完的时候

执行栈
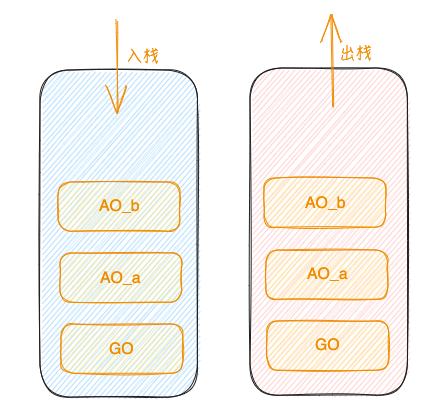
伪代码
方便理解, 作用域机制
// 0. 预编译开始, 初始化作用域链和GO
var $scopeChain = [
GO,
];
// 1. a 函数被定义
a['[[scope]]'] = $scopeChain; // [GO]
// 2. a函数被执行
$scopeChain.unshift(Ao_a); // [AO_a, GO]
// 3. a函数执行后, b 函数被定义
b['[[scope]]'] = $scopeChain; // [AO_a, GO]
// 4. b函数数被执行
$scopeChain.unshift(Ao_b); // [AO_b, AO_a, GO]
// 5. b函数执行完之后
$scopeChain.shift(); // [AO_a, GO]
// 6. a函数执行完之后
$scopeChain.shift(); // [GO]
// 7. 代码全部执行完
$scopeChain.shift(); // []什么是闭包
MDN 文档 推荐阅读
广义的闭包
广义的闭包是一个函数和它的周边词法环境的引用的组合就称之为闭包, 简单的理解就是: 每个函数都是一个闭包, 也就是MDN文档上说的内容
《你不知道的JavaScript》中这样总结道: 当函数可以记住并访问所在的词法作用域时, 就产生了闭包, 即使函数是当前词法作用域之外执行
而我们在日常开发中所说的 "闭包" 其实是指 实用的闭包
实用的闭包
实用的闭包也是闭包的一种, 只不过与普通的闭包不同的是, 它会引用外界的变量, 导致在在执行完之后不会立即销毁, 这样的特性就会导致:
- 好处: 延长变量的生命周期, 等到我想要释放这个变量的时候在释放
- 坏处: 可能会导致
内存泄露
// 防抖: n秒后执行该方法, 如果重复触发(n秒内), 就重新计时
function debounce(func, wait = 1000, thisArg = null) {
let timer;
return function (...args) {
// 如果不清除定时器, 就会让这个 timer 变量一直存在, 无法让垃圾回收机制释放这个变量对应的内存
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(func.bind(thisArg, ...args), wait);
};
}闭包的作用
利用闭包的特性, 我们可以做以下几点:
- 私有方法/属性, 不会污染全局作用域
- 延长变量的生命周期
function createCounter() {
const count = 0;
return {
increment() {
return count++;
},
decrement() {
return count--;
},
};
}
const counter = createCounter();IIFE - 立即执行的函数表达式
什么是 IIFE?
- IIFE 其实是
immediately-invoked function expression的缩写, 翻译为立即执行的函数表达式 - 自动执行
- 执行完之后, 立即销毁
- 以下两种写法都是可以的:
(function () {
// codes
})();
(function () {
// codes
})();IIFE 参数
(function (a, b) {
console.log(a + b); // 6
})(2, 4);IIFE 返回值
var num = (function () {
return a + b;
})(2, 4);
console.log(num); // 6函数的执行
()括号中包括的一定是表达式,(1)(function(){})(function test(){})- 只有表达式, 才能被执行符号执行
- 将函数声明强行转表达式:
+-!||&&==
(function(){ console.log(1) })(); // (function(){}) 这是个表达式
var test = function test() { // 这是个赋值表达式, 所以也能执行, 先赋值, 后执行
console.log(1);
}();
+function test2() { // 转换表达式(转number) 所以可以正常执行
console.log(2)
}();
-function test3() { // 转换表达式(转number) 所以可以正常执行
console.log(3)
}();
!function test4() { // 转换表达式(转boolean) 所以可以正常执行
console.log(4)
}();
1 && function test4() { // 条件判断表达式, 所以可以正常执行
console.log(4)
}();
0 || function test4() { // 条件判断表达式, 所以可以正常执行
console.log(4)
}();
"hello" === function () { // 条件判断表达式, 所以可以正常执行
console.log('sdf');
}();
// 语法错误(SyntaxError): 这不是个表达式, 这是个函数声明
function fn() {
console.log(3)
}();
function fn2(){ // 不会报错, 虽然test5, 不会直接被执行, 但是会被声明
console.log(5);
}(true);
/*
因为js语法是允许一行的末尾可以不使用;结尾的, 所以,
js引擎会把代码解析成这样2个语句, 所以不会报错
function fn2(){
console.log(5);
}; (true);
*/IIFE 的作用
- 模块化: 在没有 ES6 的时候, 都使用这种方式来实现模块化, 保证全局作用域不被污染
- 函数式编程中的
惰性函数
(function (win) {
// filename: bindEvents.js
win.bindEvents = function () {
// ...some codes
};
})(window);
(function (win) {
// filename: init.js
win.init = function () {
this.bindEvents();
// ...other codes
};
win.init();
})(window);练习
练习1
Q: 问控制台会打印什么 A: 打印10个 10
function test() {
var fns = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fns[i] = function () {
console.info(i);
};
}
// 执行完 for 循环的时候, i = 10
return fns;
}
var arr = test();
for (var i = 0, l = arr.length; i < l; i++) {
// 这个位置执行的时候, 函数内部找不到i就会向上级作用域去找变量i, 此时i的值是10
arr[i]();
}练习2
Q: 问控制台打印什么 A: 打印 0-9
function test() {
var fns = [];
for (var =0; i<10; i++) {
(function(num) { // for 循环一次, 就立即执行一次, 此时i是多少num就是多少
arr[num] = function() {
console.log(num);
};
})(i);
}
}练习3
Q: 问控制台打印什么 A: 打印 0-9
function test() {
var fns = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// ---- 注意这一行代码用的是 let, let是没有变量提升的 -----
fns[i] = function () {
console.info(i);
};
}
return fns;
}
var arr = test();
for (var i = 0, l = arr.length; i < l; i++) {
arr[i]();
}练习4
Q: 控制台会打印出什么? A: 10undefined
var a = 10;
if (function b() {}) {
a += typeof b;
}
console.log(a);解题思路: (function b(){}) 这是个表达式, 而且值肯定 不是false 表达式会忽略函数名, 所以打印的是 10undefined
练习5
写个闭包记录函数的调用次数, 每执行一次就把 执行次数+1
var test = (function () {
var counter = 0;
return function () {
counter++;
console.info(counter);
};
})();
test(); // 1
test(); // 2
test(); // 3写个方法, 一个班级,学生名字保存在数组中,两个方法写在对象中,一个加入班级, 一个离开班级, 每次加入或离开都打印出学生名单
var studentMgr = (function () {
var students = ['张三', '李四'];
var manager = {};
manager.joinClass = function (name) {
students.push(name);
console.info(students);
};
manager.leaveClass = function (name) {
for (var i = 0, l = students.length; i < l; i++) {
if (name === students[i]) {
students.splice(i, 1);
break;
}
}
console.info(students);
};
return manager;
})();
studentMgr.joinClass('zs');
studentMgr.joinClass('ls');
studentMgr.leaveClass('zs');