基础知识
随着h5的应用范围越来越广, UI也随着发生了翻天覆地的变化, 这就导致了, 不是所有的布局都是规规矩矩的这种布局
有的需要一个元素根据一个参照物, 偏移指定距离来显示:
如 图标和图片的位置:

注:除了静态定位以外的其他定位会让元素脱离文档流
定位类型
| 取值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| static | 默认行为, 参考文档流 |
| relative | 相对定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位 |
| sticky | 粘性定位 |
参照物
参照物是根据定位类型来决定的, 比如:
- 绝对定位是以
第一个相对定位的祖先元素作为参照物 - 相对定位是以
元素自身在正常文档流中的位置进行定位的 - 固定定位就是以
浏览器的可视区域来做参照物 - 粘性定位是以
元素所在的滚动容器来做参照物
偏移距离
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| top | 参照物上边偏移量 |
| bottom | 参照物下边偏移量 |
| left | 参照物左边偏移量 |
| right | 参照物右边偏移量 |
静态定位 static
元素默认的定位方式就是静态定位, 也就是说, 在正常文档流钟的元素都是静态定位
相对定位 relative
css
#app {
border: 1px solid blue;
}
.box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background: #f00;
position: relative;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<title>JavaScript</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./styles.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
绝对定位 absolute
css
#app {
border: 1px solid blue;
margin: 20px;
}
.outer {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: relative;
top: 0;
left: 0; /* 横向,纵向的位置相当于和文档流的位置一样 */
background-color: #f00;
/*
如果注释: position: absolute;
那么 div.inner 在绝对定位的时候, 参照物就会继续向上寻找,
直到找到一个元素为相对定位的祖先元素时, 以这个祖先元素为
参照物, 如果没有找到, 那么就以浏览器的可视窗口为参照物
*/
}
.inner {
position: absolute;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
top: 15px;
left: 30px;
background-color: #0f0;
}html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<title>JavaScript</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./styles.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="outer">
<div class="inner"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>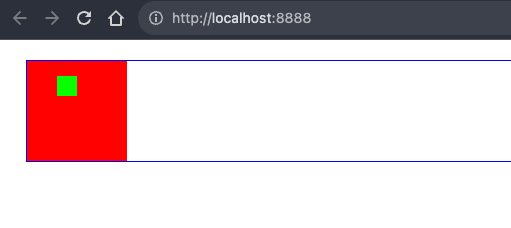
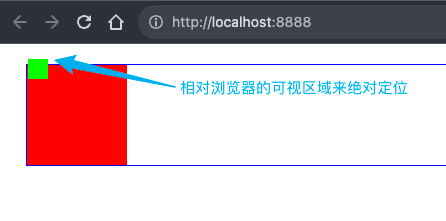
固定定位 fixed
css
.high-box {
height: 5000px;
width: 100%;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#app {
border: 1px solid blue;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: fixed;
top: 20px;
left: 20px;
}html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<title>JavaScript</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./styles.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="high-box"></div>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>
黏性定位 sticky
css
#app {
width: 100%;
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #000;
overflow: auto;
}
.contents {
height: 1000px;
background-color: #ccc;
}
.sticky-box {
width: 500px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #f00;
position: sticky;
top: 10px;
left: 10px;
}html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="zh-cn">
<head>
<title>JavaScript</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./styles.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="contents">some contents</div>
<div class="sticky-box"></div>
<div class="contents">some contents</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>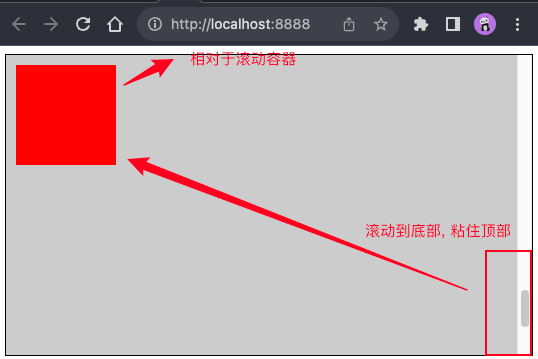
纵向层级 z-index
因为一旦定位就会脱离文档流, 那么如果两个元素定位的位置重合, 那么该显示哪个元素呢?
如果元素重叠在一起, 可以使用 z-index 控制元素的上下层级, 数值越大越在上面
这个不好描述, 直接看图吧, 一图胜千言
